What is the Internet?
To explain what the web is, we’ll begin from the networks.
What is a Network?
Most of the time, computer users work on their own with their computer connected to nada additional exciting than a printer. However, it's continually been potential to attach 2 PCs with a chunk of wire so they'll communicate – typically simply to transfer files.
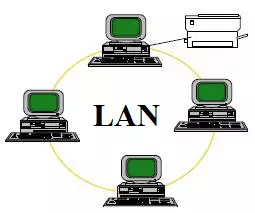
Local Area Networks :
It is sensible, most frequently for monetary reasons however additionally for others, to network teams of computers wherever they share a typical employment. All the computers in Associate in Nursing body workplace, all the computers to try and do with a particular ward or discipline. Networking computers means the individuals victimisation them will share files simply, send one another messages and share every other’s printers. this concept has developed into Local Area Networks (LANs). These days most organisations have {a local|an space|a neighborhood} area network. LANs is as little as only one shared workplace or as massive as an entire town.
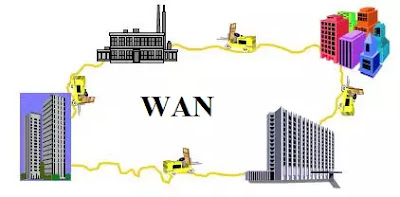
Wide Area Networks :
In some cases Associate in Nursing organisation is touch an oversized space, and you are doing not have the simple concentration of computing to supply a local area network for. during this instance computers is also connected by a Wide Area Network (WAN). The distinction between a WAN and a local area network is partially one amongst scale (although this is often relative) however additionally relates to the technology. With a local area network you may generally get a quick network which will network computer file servers. With a WAN the network can typically be abundant slower and can typically involve some digital computer because the server instead of a computer.
Combinations of Networks :
LANs and WANs don't seem to be reciprocally exclusive. if truth be told they mix fine along. several organisations currently have each, wherever a WAN has been created by connecting up a series of LANs. a decent example of this is often the tutorial Community. each University has it’s own local area network providing email, printing, file sharing and alternative facilities. Then each University is connected to the Joint Academic Network (JANET) that could be a WAN running the length of the country.
Internet -
Large fleas have very small fleas on their backs to bite them, false fleas have small and perpetual fleas. Nice fleas have larger fleas, upon whose backs they ride on, The larger fleas have larger however, and larger however, and so on.
If you are taking the principle of little, domestically managed, networks connected up to create a bigger network, that successively is connected up to create a bigger network, and so on, you get some plan of what the net is. Physically it's simply a group of LANs and WANs that are connected up at a national and international level.
The Internet is quite this, however. It not solely is that the physical wire, however conjointly however data is distributed from one laptop to a different. Take the instance of creating a road journey. If you're causation somebody in a very automobile to travel somewhere, you'll do one in all 2 things:
- Give them precise written details of the way to get to their destination. As they need no different suggests that of finding their manner they're going to have to be compelled to continue your directions notwithstanding they will see roadworks ahead.
- Give them a map and allow them to realize their own manner. If roadworks, or another blockage happens then the person will either browse the map and compute a contemporary route, alternatively follow the diversion signs.
Now data is additional intelligent and might compute its own route, thus if there's a hold-up it'll try to get through another manner. It’s all rather clever, and was made-up by the yankee Defence business WHO asked “If somebody born a awfully giant bomb on our network, wouldn't it still function?”. The intelligent data transfer a mechanism known as the Internetworking Protocol (hence “Internet”)
What does one do with a Network?
To get on to the net you have got to own associate identification distinctive to you known as your username. everybody WHO connects to the net includes a username, and if you have got their username and also the name of the machine they log into you'll send a message to it username and that they can receive it after they next log in. this technique is termed electronic message or email for brief.
The basic ideas behind email parallel those of standard mail. You send mail to individuals at their specific addresses. In turn, they write to you at your email address. you'll buy the electronic equivalent of magazines and newspapers. Sooner or later, you’ll most likely even get electronic junk.
Email has 2 distinct benefits over regular mail. the foremost obvious is speed. rather than many days, your message will reach the opposite facet of the planet in hours, minutes or maybe seconds. the opposite advantage is that after you master the fundamentals, you’ll be ready to use email to access databases and file libraries moreover as transfer files and programs.
Email conjointly has benefits over the phonephone. You send your message once it’s convenient for you. Your recipients respond at their convenience. No additional frustration while you phone somebody who’s out, then they phone you back while you’re out. And whereas a call across the country or round the world will quickly lead to Brobdingnagian phone bills, email allows you to exchange huge amounts of mail for under a number of pennies – notwithstanding the opposite person is on the opposite facet of the planet.
Email is your association to assist – your internet lifeline. Infobahn will typically appear a frustrating place! notwithstanding however onerous you are attempting, notwithstanding wherever you look, you only may not be ready to realize the solution to no matter is inflicting you issues. however after you skills to use email, assistance is typically simply a number of keystrokes away: you'll raise your computer user or a fan for facilitate in associate email message.
Even if you employ the net for no different purpose, email makes obtaining a association worthy all by itself. terribly quickly you’ll end up writing to friends WHO area unit on the net, contacting colleagues curious about similar skilled areas all around the world, discussing politics and posing for recommendation on the way to use a number of the code on your laptop. it's terribly powerful and implausibly low-cost.
Many-to-Many Discussions :
Usenet is extremely like email, in this you compose a message and send it somewhere. However, rather than being sent to someone the message is distributed to your native Usenet system. That manner the messages area unit hold on centrally, once, for everybody to browse, instead of have each message preventative up every individual user’s email area. The native system is in constant contact with different Usenet systems round the world, they compare messages and exchange those they don’t have. That manner your message to the native system in Bradford-on-Avon gets passed from laptop to laptop around the world for everybody to examine whenever they access their native Usenet system.
The basic building block of Usenet is that the newsgroup, that could be a assortment of messages with a connected theme (on different networks, these would be known as conferences, forums, bboards or special-interest groups). There area unit currently several thousands of those newsgroups, in many completely different languages, covering everything from art to zoological science, from phantasy to African nation.
The basic ideas behind email parallel those of standard mail. You send mail to individuals at their specific addresses. In turn, they write to you at your email address. you'll buy the electronic equivalent of magazines and newspapers. Sooner or later, you’ll most likely even get electronic junk.
Email has 2 distinct benefits over regular mail. the foremost obvious is speed. rather than many days, your message will reach the opposite facet of the planet in hours, minutes or maybe seconds. the opposite advantage is that after you master the fundamentals, you’ll be ready to use email to access databases and file libraries moreover as transfer files and programs.
Email conjointly has benefits over the phonephone. You send your message once it’s convenient for you. Your recipients respond at their convenience. No additional frustration while you phone somebody who’s out, then they phone you back while you’re out. And whereas a call across the country or round the world will quickly lead to Brobdingnagian phone bills, email allows you to exchange huge amounts of mail for under a number of pennies – notwithstanding the opposite person is on the opposite facet of the planet.
Email is your association to assist – your internet lifeline. Infobahn will typically appear a frustrating place! notwithstanding however onerous you are attempting, notwithstanding wherever you look, you only may not be ready to realize the solution to no matter is inflicting you issues. however after you skills to use email, assistance is typically simply a number of keystrokes away: you'll raise your computer user or a fan for facilitate in associate email message.
Even if you employ the net for no different purpose, email makes obtaining a association worthy all by itself. terribly quickly you’ll end up writing to friends WHO area unit on the net, contacting colleagues curious about similar skilled areas all around the world, discussing politics and posing for recommendation on the way to use a number of the code on your laptop. it's terribly powerful and implausibly low-cost.
Many-to-Many Discussions :
If you wish to own a personal discussion with somebody a couple of specific topic, then email is ideal for that. It’s a matched communication tool. However, you typically need to own a many-to-many discussion, such as you would in a very meeting. Email will do that however isn't terribly convenient. Instead there's a typical system for several to several discussions known as Usenet.
Usenet is extremely like email, in this you compose a message and send it somewhere. However, rather than being sent to someone the message is distributed to your native Usenet system. That manner the messages area unit hold on centrally, once, for everybody to browse, instead of have each message preventative up every individual user’s email area. The native system is in constant contact with different Usenet systems round the world, they compare messages and exchange those they don’t have. That manner your message to the native system in Bradford-on-Avon gets passed from laptop to laptop around the world for everybody to examine whenever they access their native Usenet system.
The basic building block of Usenet is that the newsgroup, that could be a assortment of messages with a connected theme (on different networks, these would be known as conferences, forums, bboards or special-interest groups). There area unit currently several thousands of those newsgroups, in many completely different languages, covering everything from art to zoological science, from phantasy to African nation.
Some public-access systems, usually those that job through menus, try and build it easier by dividing Usenet into many broad classes. select one in all those and you’re given an inventory of newsgroups in this class. Then choose the newsgroup you’re curious about and begin reading.
Other systems allow you to compile your own “reading list” in order that you simply see messages in conferences you wish. In each cases, newsgroups area unit organized in a very specific hierarchy devised within the early Nineteen Eighties. Newsgroup names begin with one in all a series of broad topic names. for instance, newsgroups starting with “comp.” area unit regarding computer-related topics. These broad topics area unit followed by a series of additional targeted topics (so that “comp.unix” teams area unit restricted to discussion regarding UNIX). the most hierarchies are:
Other systems allow you to compile your own “reading list” in order that you simply see messages in conferences you wish. In each cases, newsgroups area unit organized in a very specific hierarchy devised within the early Nineteen Eighties. Newsgroup names begin with one in all a series of broad topic names. for instance, newsgroups starting with “comp.” area unit regarding computer-related topics. These broad topics area unit followed by a series of additional targeted topics (so that “comp.unix” teams area unit restricted to discussion regarding UNIX). the most hierarchies are:
- bionet: analysis biology
- bit.listserv: Conferences originating as Bitnet mailing lists
- biz: Business
- comp: Computers and connected subjects
- misc: Discussions that don’t work anyplace else
- news: News regarding Usenet itself
- rec: Hobbies, games and recreation
- sci: Science aside from analysis biology
- soc: “Social” teams, typically ethnically connected
- talk: Politics and connected topics
- alt: moot or uncommon topics; not carried by all sites



0 Comments
I will be there for your help...